Dijkstra’s algorithm Definition
Dijkstra’s algorithm (or Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First algorithm, SPF algorithm) is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph, which may represent, for example, road networks. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956 and published three years later.
The algorithm exists in many variants; Dijkstra’s original variant found the shortest path between two nodes, but a more common variant fixes a single node as the “source” node and finds shortest paths from the source to all other nodes in the graph, producing a shortest-path tree.
Example By Image
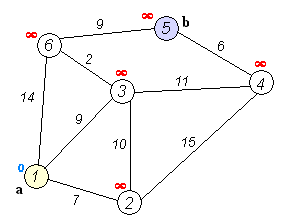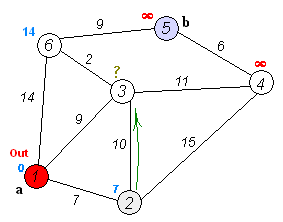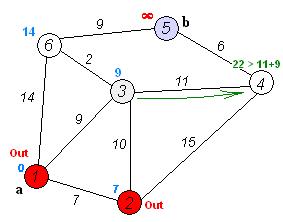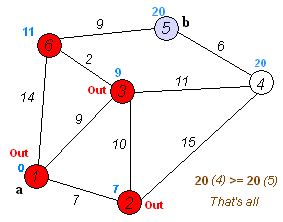
Source Code by C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<string.h>
//Structure for storing a graph
struct Graph{
int vertexNum;
int** edges;
};
//Constructs a graph with V vertices and E edges
void createGraph(struct Graph* G,int V){
G->vertexNum = V;
G->edges =(int**) malloc(V * sizeof(int*));
for(int i=0; i<V; i++){
G->edges[i] = (int*) malloc(V * sizeof(int));
for(int j=0; j<V; j++)
G->edges[i][j] = INT_MAX;
G->edges[i][i] = 0;
}
}
//Adds the given edge to the graph
void addEdge(struct Graph* G, int src, int dst, int weight){
G->edges[src][dst] = weight;
}
//Utility function to find minimum distance vertex in mdist
int minDistance(int mdist[], int vset[], int V){
int minVal = INT_MAX, minInd ;
for(int i=0; i<V;i++)
if(vset[i] == 0 && mdist[i] < minVal){
minVal = mdist[i];
minInd = i;
}
return minInd;
}
//Utility function to print distances
void print(int dist[], int V){
printf("\nVertex Distance\n");
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
if(dist[i] != INT_MAX)
printf("%d\t%d\n",i,dist[i]);
else
printf("%d\tINF",i);
}
}
//The main function that finds the shortest path from given source
//to all other vertices using Dijkstra's Algorithm.It doesn't work on negative
//weights
void Dijkstra(struct Graph* graph, int src){
int V = graph->vertexNum;
int mdist[V]; //Stores updated distances to vertex
int vset[V]; // vset[i] is true if the vertex i included
// in the shortest path tree
//Initialise mdist and vset. Set distance of source as zero
for(int i=0; i<V; i++)
mdist[i] = INT_MAX, vset[i] = 0;
mdist[src] = 0;
//iterate to find shortest path
for(int count = 0; count<V-1; count++){
int u = minDistance(mdist,vset,V);
vset[u] = 1;
for(int v=0; v<V; v++){
if(!vset[v] && graph->edges[u][v]!=INT_MAX && mdist[u] + graph->edges[u][v] < mdist[v])
mdist[v] = mdist[u] + graph->edges[u][v];
}
}
print(mdist, V);
return;
}
//Driver Function
int main(){
int V,E,gsrc;
int src,dst,weight;
struct Graph G;
printf("Enter number of vertices: ");
scanf("%d",&V);
printf("Enter number of edges: ");
scanf("%d",&E);
createGraph(&G,V);
for(int i=0; i<E; i++){
printf("\nEdge %d \nEnter source: ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&src);
printf("Enter destination: ");
scanf("%d",&dst);
printf("Enter weight: ");
scanf("%d",&weight);
addEdge(&G, src, dst, weight);
}
printf("\nEnter source:");
scanf("%d",&gsrc);
Dijkstra(&G,gsrc);
return 0;
}